Structure de Pegase
Introduction
Pegase est un modèle intégré bassin hydrographique / rivières qui permet de calculer de façon déterministe la qualité des eaux des rivières en fonction des rejets et apports de pollution, pour différentes situations hydrologiques et en mode non-stationnaire sur plusieurs années; il permet également de calculer de façon prévisionnelle les améliorations de la qualité de l’eau qui résultent d’actions d’épuration ou de réduction des rejets.

Pegase peut traiter plusieurs milliers de rivières simultanément et la superficie des bassins hydrographiques considérés peut atteindre plusieurs dizaines de milliers de km2; Pegase permet également d’effectuer des simulations fines sur un sous-ensemble du bassin versant considéré (par exemple, sur une seule rivière d’un bassin versant de quelques dizaines de km2).
Pegase fait partie d’une nouvelle génération de modèles, s’appuyant sur une représentation détaillée de la dynamique du système, notamment le calcul explicite de l’évolution des différentes biomasses. En outre, la structure du modèle Pegase est telle que la plupart des paramètres ont une signification physique ou biologique (par exemple taux maximal de croissance) et peuvent donc être calibrés séparément par des mesures expérimentales bien ciblées. Un des avantages est que Pegase peut donc être employé avec peu de modifications et de calibrations pour différentes situations hydrologiques et différents réseaux hydrographiques.
Structuration du modèle
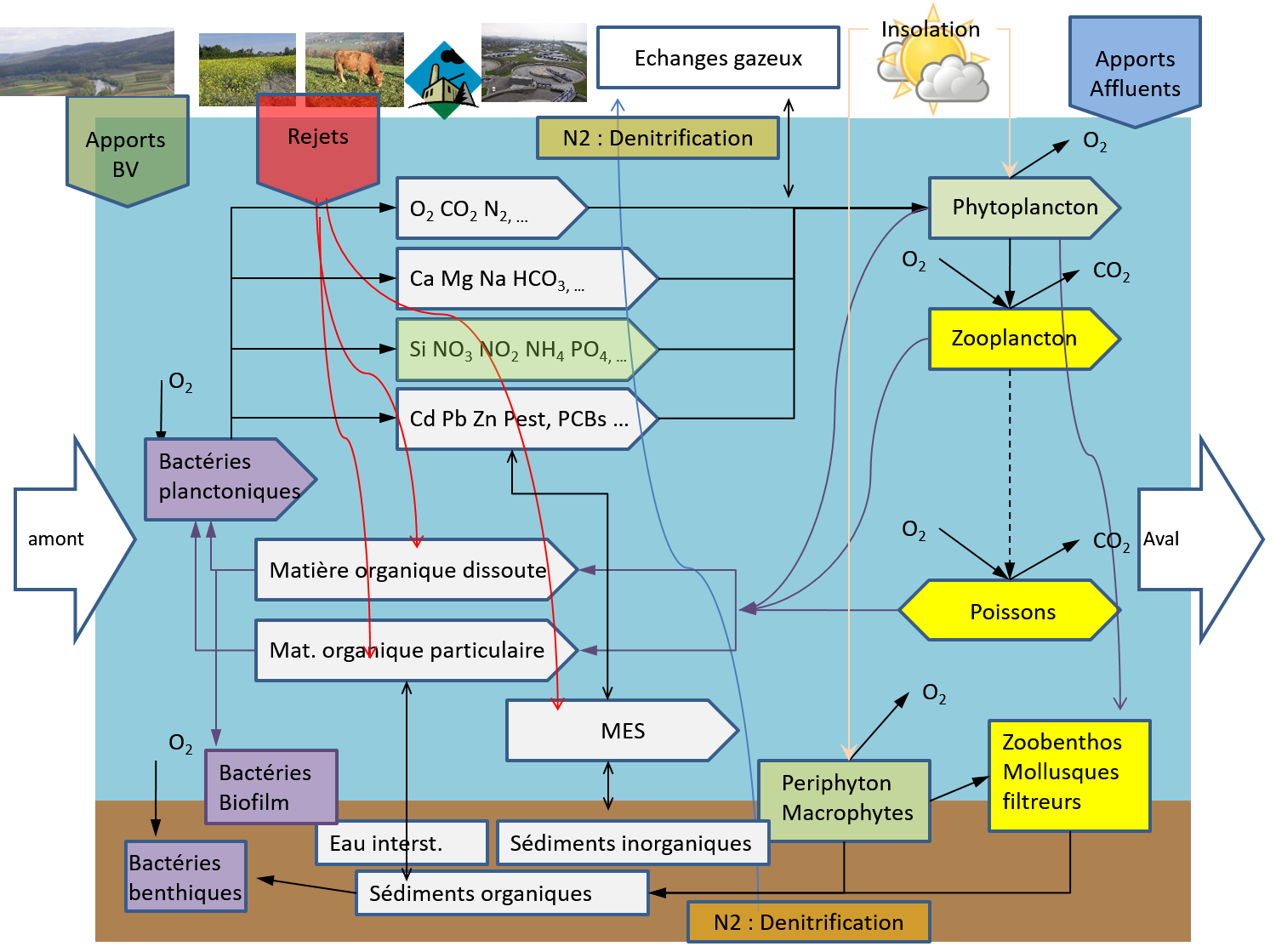
Compte tenu des processus à représenter, Pegase est structuré comme une suite de cinq sous-modèles, dont les fonctions sont les suivantes :
- Le sous-modèle rejets représente de façon structurée les rejets urbains, les rejets industriels, le rôle des stations d’épuration, les rejets dus aux activités d’élevage et les apports diffus des sols ; il calcule les apports et rejets au réseau des rivière modélisé
- Le sous-modèle hydrologique et hydrodynamique calcule les débits et les autres paramètres hydrodynamiques (vitesses, hauteurs d’eau, ...) en tous les nœuds du réseau des rivières, et à tout moment (valeurs journalières au minimum) à partir des caractéristiques morphométriques des rivières (pentes, largeurs, barrages, ...) et des débits mesurés en une ou plusieurs stations de mesure
- Le sous-modèle thermique calcule la température de l’eau, se basant sur la température mesurée en des points discrets et les valeurs des différents rejets thermiques
- Le sous-modèle biologique calcule :
- à partir de la lumière (irradiance en surface) comme principale donnée d’entrée, le développement des biomasses phytoplanctoniques
- le développement des biomasses bactériennes
- le bilan de la matière organique (apports par les sols, les rejets domestiques, les rejets industriels et production interne par l’écosystème)
- les flux de nutriments
- enfin, le bilan en oxygène (production par les végétaux, consommation par les respirations, réaération à travers la surface)
- Le sous-modèle micropolluants calcule l’évolution des micropolluants rejetés, ce qui implique une représentation des processus de sédimentation appropriée
Processus représentés
Parmi les principaux processus et fonctionnalités intégrés dans le modèle Pegase, on peut citer :
- le calcul explicite de la production primaire (biomasse phytoplanctonique) à l’aide d’un sous-modèle multi-espèces
- le calcul explicite des mécanismes d’autoépuration (calcul des biomasses bactériennes et de leur activité)
- le calcul des micropolluants (métaux lourds, …)
- le calcul d’indices de qualité physico-chimiques (par exemple les SEQ-Eau français)
Utilisation du modèle
Pegase peut être utilisé suivant deux modes principaux :
- le mode « stationnaire », dans lequel les conditions hydrométéorologiques (débits, températures, insolations) sont considérées comme constantes. Ce mode permet de réaliser des simulations hydrométéorologiques représentatives d’un régime caractéristique (année humides, centile sur débit, …) qu’il est facile de visualiser et comparer avec d’autres simulations
- le mode « non stationnaire », dans lequel les conditions hydrométéorologiques varient chaque jour et permettent donc de calculer des évolutions annuelles des concentrations mesurées sur l’ensemble du réseau hydrographique modélisé
L’utilisation du modèle a été fortement facilitée ces dernières années dans le cadre du programme « Pegase Opera » (pour « rendre le programme Pegase plus opérationnel ») réalisé avec l’aide des utilisateurs de Pegase, pour aboutir à la suite logicielle PegOpera.
 Aquapole
AquapoleQuartier Polytech 1
Allée de la découverte, 11
4000 Liège
BELGIQUE
